硫化橡胶体积表面电阻率测量仪 试样处置
电极之间或测量电极与大地之间的杂散电流对于测试仪器的读数没有明显的影响这一点很重要。测试时加电极到试样上和安放试样时均要极为小心,以免可能产生对测试结果有不良影响的杂散电流通道。
测量表面电阻时,不要清洗表面,除非另有协议或规定。除了同二材料的另一个试样的未被触模过的表面可触及被测试样外,表面被测部分不应被任何东西触及。
硫化橡胶体积表面电阻率测量仪 技术指标
1、电阻测量范围:1?104Ω~1?1018Ω。
2、电流测量范围为:2?10-4A~1?10-16A
3、双表头显示:3.1/2位LED显示
4、内置测试电压:10V、50V、100V、250、500、1000V
5、基本准确度:1% (*注)
6、使用环境: 温度:0℃~40℃,相对湿度<80%
7、机内测试电压:10/50/100/250/500/1000V任意切换
8、供电形式:AC 220V,50HZ,功耗约5W
9、仪器尺寸:285mm? 245mm? 120 mm
10、质量: 约2.5KG
防止漏电流的影响:对于高电阻材料,只有采取保护技术才能去除漏电流对测量的影响。保护技术就是在引起测量误差的漏电路径上安置保护导体,截住可能引起测量误差的杂散电流,使之不流经测量回路或仪表。保护导体连接在一起构成保护端,通常保护端接地。测量体积电阻时,三电极系统的保护极就是保护导体。此时要求保护电极和测量电极间的试样表面电阻高于与它并联元件的电阻10~100倍。线路接好后,应首先检查是否存在漏电。此时断开与试样连接的高压线,加上电压。如在测量灵敏度范围内,测量仪器指示的电阻值为无限大,则线路无漏电,可进行测量。
温度和湿度:固体绝缘材料的绝缘电阻率随温度和湿度的升高而降低,特别是体积电阻率随温度改变而变化非常大。因此,电瓷材料不但要测定常温下的体积电阻率,而且还要测定高温下的体积电阻率,以评定其绝缘性能的好坏。由于水的电导大,随着湿度增大,表面电阻率和有开口孔隙的电瓷材料的体积电阻率急剧下降。因此,测定时应严格地按照规定的试样处理要求和测试的环境条件下进行。
典型应用
1.测量防静电鞋、导电鞋的电阻值
2、测量防静电材料的电阻及电阻率
3、测量计算机房用活动地板的系统电阻值
4、测量绝缘材料电阻(率)
5、光电二极管暗电流测量
6、物理,光学和材料研究
电阻率的计算公式为:
ρL
R= —
S
ρ为电阻率——常用单位Ω?mm2/m
S为横截面积——常用单位㎡
R为电阻值——常用单位Ω
L为导线的长度——常用单位m
电阻定律
导体的电阻R跟它的长度L、电阻率ρ成正比,跟它的横截面积S成反比,这个规律就叫电阻定律(law of resistance),公式为R=ρL/S。其中ρ:制成电阻的材料的电阻率,L:绕制成电阻的导线长度,S:绕制成电阻的导线横截面积,R:电阻值。
公式:R=ρL/S,R=U/I
ρ——制成电阻的材料电阻率,国际单位制为欧姆?米(Ω ? m);
L——绕制成电阻的导线长度,国际单位制为米(m);
S——绕制成电阻的导线横截面积,国际单位制为平方米(m2) ;
R——电阻值,国际单位制为欧姆,简称欧(Ω);
U——电压值,国际单位制为伏特,简称伏(v);
I——电流值,国际单位制为安培,简称安(A)。
其中:
ρ叫电阻率:某种材料制成的长1米、横截面积是1平方毫米的导线的电阻,叫做这种材料的电阻率。是描述材料性质的物理量。国际单位制中,电阻率的单位是欧姆?米,常用单位是欧姆?平方毫米/米。与导体长度L,横截面积S无关,只与物体的材料和温度有关,有些材料的电阻率随着温度的升高而增大,有些反之。
电源
要求有很稳定的直流电压源。这可用蓄电油或一个整流稳压的电摞来提供。对电源的稳定度要求是由电压变化导致的电流变化与被测电流相比可忽略不计。
加到整个试样上的试验电压通常规定为100V、250V、500V、1000 V、2500 V、5000 V, 10000 V和15000 V。 常用的电压是100V、500V和1000 V。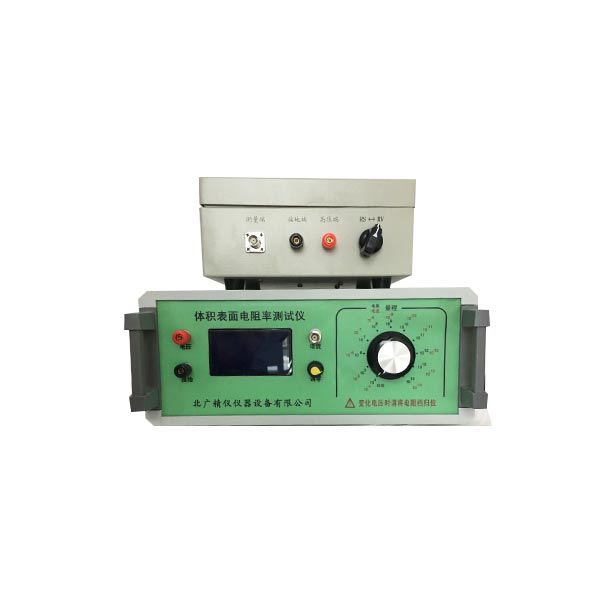
在某些情况下,试样的电阻与施加电压的极性有关
如果电阻是与极性有关的,则宜加以注明。取两次电阻值的几何平均值(对数算术平均值的反对数)作为结果。
由于试样电阻可能与电压有依存关系,因此应在报告中注明试验电压值。
power supply
Require a very stable DC voltage source. This can be provided by storing oil or a rectifier stabilized stack of electricity. The stability requirement for the power supply is that the current variation caused by voltage changes can be ignored compared to the measured current.
The test voltages applied to the entire sample are usually specified as 100V, 250V, 500V, 1000V, 2500V, 5000V, 10000V, and 15000V. The commonly used voltages are 100V, 500V, and 1000V.
In some cases, the resistance of the sample is related to the polarity of the applied voltage
If the resistance is polarity dependent, it should be noted. Take the geometric mean of two resistance values (the inverse of the logarithmic arithmetic mean) as the result.
Due to the possible dependence of sample resistance on voltage, the test voltage value should be indicated in the report.
试样
7.1体积电阻率
为测定体积电阻率,试样的形状不限,只要能允许使用第三电极来抵消表面效应引起的误差即可。对于表面泄漏可忽略不计的试样,测量体积电阻时可去掉保护,只要己证明去掉保护对结果的影响可忽略不计。
在被保护电极与保护电极之间的试样表面上的间隙要有均匀的宽度,并且在表面泄漏不致于引起测量误差的条件下间隙应尽可能的窄。lmm的间隙通常为切实可行的 小间隙。
图2及图3给出了三电极装置的例子。在测量体积电阻时,电极1是被保护电极,电极2为保护电 极,电极3为不保护电极。被保护电极的直径d1(图2)或长度l1(图3)应至少为试样厚度h的10倍,通 常至少为25mm。不保护电极的直径d4(或长度[4)和保护电极的外直径d3(或保护电极两外边缘之间 的长度[3)应该等于保护电极的内径d2(或保护电极两内边缘之间的长度lz)加上至少2倍的试样厚度。
7.2表面电阻率
为测定表面电阻率,试样的形状不限,只要允许使用第三电极来抵消体积效应引起的误差即可。推荐使用图2及图3所示的三电极装置。用电极1作为被保护电极,电极3作为保护电极,电极2作为不 保护电极。可直接测量电极1和2之间表面间隙的电阻。这样测得的电阻包括了电极1和2之间的表面电阻和这两个电极间的体积电阻。然而,对于很宽范围的环境条件和材料性能,当电极尺寸合适时, 体积电阻的影响可忽略不计。为此,对于图2和图3所示的装置,电极的间隙宽度g至少应为试样厚度 的2倍,一般说来,1mm为切实可行的 小间隙。被保护电极尺寸d1(或长度l1)应至少为试样厚度h的10倍,通常至少为25mm。
也可以使用条形电极或具有合适尺寸的其他装置。
注:由于通过试样内层的电流的影响,表面电阻率的计算值与试样和电极的尺寸有很大的关系,因此,为了测定时可进行比较,推荐使用与图2所示的电极装置的尺寸相一致的试样,其中d1= 50 mm, d2 = 60 mm, ds = 80 mm
sample
7.1 Volume resistivity
To determine the volume resistivity, the shape of the sample is not limited, as long as it allows the use of a third electrode to offset the errors caused by surface effects. For samples with negligible surface leakage, the protection can be removed when measuring the volume resistance, as long as it has been proven that removing the protection has negligible effects on the results.
The gap on the surface of the sample between the protected electrode and the protective electrode should have a uniform width, and the gap should be as narrow as possible under the condition that surface leakage does not cause measurement errors. The clearance of LMM is usually a feasible small clearance.
Examples of three electrode devices are shown in Figures 2 and 3. When measuring volume resistance, electrode 1 is the protected electrode, electrode 2 is the protected electrode, and electrode 3 is the unprotected electrode. The diameter d1 (Figure 2) or length l1 (Figure 3) of the protected electrode should be at least 10 times the thickness h of the specimen, typically at least 25mm. The diameter d4 (or length [4]) of the unprotected electrode and the outer diameter d3 (or length [3] between the two outer edges of the protected electrode) should be equal to the inner diameter d2 (or length lz between the two inner edges of the protected electrode) of the protected electrode plus at least twice the thickness of the sample.
7.2 Surface resistivity
To determine surface resistivity, the shape of the sample is not limited, as long as it allows the use of a third electrode to offset errors caused by volume effects. Recommend using the three electrode device shown in Figures 2 and 3. Use electrode 1 as the protected electrode, electrode 3 as the protective electrode, and electrode 2 as the unprotected electrode. The resistance of the surface gap between electrodes 1 and 2 can be directly measured. The resistance measured in this way includes the surface resistance between electrodes 1 and 2 and the volume resistance between these two electrodes. However, for a wide range of environmental conditions and material properties, the influence of volume resistance can be ignored when the electrode size is appropriate. Therefore, for the devices shown in Figures 2 and 3, the gap width g of the electrodes should be at least twice the thickness of the sample. Generally speaking, 1mm is a feasible small gap. The size d1 (or length l1) of the protected electrode should be at least 10 times the thickness h of the sample, usually at least 25mm.
Strip electrodes or other devices with appropriate dimensions can also be used.
Note: Due to the influence of the current passing through the inner layer of the sample, the calculated value of surface resistivity is closely related to the size of the sample and electrode. Therefore, for comparison during measurement, it is recommended to use a sample with the same size as the electrode device shown in Figure 2, where d1=50 mm, d2 = 60 mm, ds = 80 mm
工作原理
根据欧姆定律,被测电阻Rx等于施加电压V除以通过的电流I。传统的高阻计的工作原理是测量电压V固定,通过测量流过取样电阻的电流I来得到电阻值。从欧姆定律可以看出,由于电流I是与电阻成反比,而不是成正比,所以电阻的显示值是非线性的,即电阻无穷大时,电流为零,即表头的零位处是∞,其附近的刻度非常密,分辨率很低。整个刻度是非线性的。又由于测量不同的电阻时,其电压V也会有些变化,所以普通的高阻计是精度差、分辨率低。
本仪器是同时测出电阻两端的电压V和流过电阻的电流I,通过内部的大规模集成电路完成电压除以电流的计算,然后把所得到的结果经过A/D转换后以数字显示出电阻值,即便是电阻两端的电压V和流过电阻的电流I是同时变化,其显示的电阻值不象普通高阻计那样因被测电压V的变化或电流I的变化而变,所以,即使测量电压、被测量电阻、电源电压等发生变化对其结果影响不大,其测量精度很高,从理论上讲其误差可以做到零,而实际误差可以做到千分之几或万分之几。
影响体积电阻率和表面电阻率测试的主要因素是温度和湿度、电场强度、充电时间及残余电荷等。体积电阻率可作为选择绝缘材料的一个参数,电阻率随温度和湿度的变化而显著变化。体积电阻率的测量常常用来检查绝缘材料是否均匀,或者用来检测那些能影响材料质量而又不能用其他方法检测到的导电杂质。
绝缘材料用于电气系统的各部件相互绝缘和对地绝缘,固体绝缘材料还起机械支撑作用。一般希望材料有尽可能高的绝缘电阻,并具有合适的机械、化学和耐热性能。
Working principle
According to Ohm's Law, the measured resistance Rx is equal to the applied voltage V divided by the current I passing through. The working principle of traditional high resistance meters is to measure a fixed voltage V and obtain the resistance value by measuring the current I flowing through the sampling resistor. From Ohm's Law, it can be seen that since the current I is inversely proportional to the resistance, rather than directly proportional, the displayed value of the resistance is nonlinear. That is, when the resistance is infinite, the current is zero, and the zero position of the meter head is ∞. The scales near it are very dense, and the resolution is very low. The entire scale is non-linear. Moreover, due to the variation in voltage V when measuring different resistances, ordinary high resistance meters have poor accuracy and low resolution.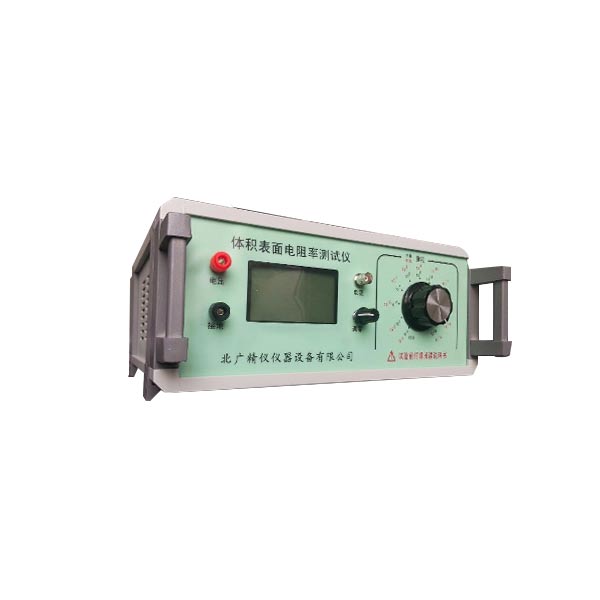
This instrument simultaneously measures the voltage V across the resistor and the current I flowing through the resistor. The voltage divided by the current is calculated through an internal large-scale integrated circuit, and the obtained result is then converted into a digital display of the resistance value through A/D conversion. Even if the voltage V across the resistor and the current I flowing through the resistor change simultaneously, the displayed resistance value does not change due to changes in the measured voltage V or current I like a regular high resistance meter. Therefore, even if changes in the measured voltage, measured resistance, power supply voltage, etc. do not have a significant impact on its results, its measurement accuracy is very high. Theoretically, its error can be zero, while the actual error can reach a few thousandths or tens of thousands.
The main factors affecting the testing of volume resistivity and surface resistivity are temperature and humidity, electric field strength, charging time, and residual charge. Volume resistivity can be used as a parameter for selecting insulation materials, and resistivity varies significantly with temperature and humidity. The measurement of volume resistivity is often used to check the uniformity of insulation materials or to detect conductive impurities that can affect material quality but cannot be detected by other methods.
Insulation materials are used for mutual insulation and ground insulation of various components in electrical systems, and solid insulation materials also serve as mechanical support. Generally, it is desirable for materials to have the highest possible insulation resistance and appropriate mechanical, chemical, and heat resistance properties.
条件处理
试样的处理条件取决于被试材料,这些条件应在材料规范中规定。
推荐按GB/T 10580一2003进行条件处理;由各种盐溶液所产生的相对温度在IEC 60260中给出。
可以采用机械蒸发系统。
体积电阻率和表面电阻率都对温度变化特别敏感。这种变化是指数式的。因此必须在规定的条件下来测量试样的体积电阻和表面电阻。由于水分被吸收到电介质内是相对缓慢的过程,因此测定温度对体积电阻率的影响需要延长处理期。吸收水分后通常会降低体积电阻。有些试样可能需要处理数月才能达到平衡。
体积电阻率与表面电阻的区别
体积电阻率和表面电阻是材料电学性能的两个重要参数,但两者针对的测试对象和应用场景不同。以下是两者的主要区别:
1. 定义与物理意义
体积电阻率(Volume Resistivity) 
体积电阻率是衡量材料内部导电性能的参数,表示单位体积材料对电流的阻碍能力。
体积电阻率反映材料本身的绝缘或导电特性,与材料的成分、结构及温度密切相关。例如,绝缘塑料的 可达12次方-16次方,而金属的 仅为 10的-6}- 10^-4次方 。
表面电阻(Surface Resistance)
表面电阻是衡量材料表面导电性能的参数,表示电流沿材料表面流动时的阻碍能力。
表面电阻受材料表面状态(如污染、湿度、氧化层)影响显著,常用于评估材料的防静电性能或漏电风险。
2. 测量方法与电极配置
-体积电阻率测量
- 电极设计:使用三电极系统(如保护环电极),确保电流仅通过材料内部,避免表面电流干扰。
- 测试标准:如 ASTM D257、IEC 60093。
- 适用场景:块状固体材料(如塑料、陶瓷、橡胶)的绝缘性能评估。
- 表面电阻测量
-电极设计:采用平行电极或同心环电极,使电流沿材料表面流动。
-测试标准:如 ASTM D4496、IEC 61340。
-适用场景:薄膜、涂层、纺织品等表面导电性能测试,或防静电材料的筛选。
3. 应用领域差异
参数
体积电阻率:
核心用途评估材料内部绝缘
典型应用电线绝缘层、电子封装材料、高压设备
关键影响因素材料成分、温度、杂质浓度
表面电阻:评估材料表面导电/防静电性能 导电性
影响因素表面清洁度、湿度、污染、氧化层
4. 实例对比
绝缘塑料板:
体积电阻率高于15次方,说明内部绝缘性能优异;
- 表面电阻可能因吸附水分而降低于12次方,表明表面存在微弱导电性。
5. 总结
体积电阻率:表征材料整体的绝缘或导电能力,是材料本征属性的体现。
表面电阻:反映材料表面的导电特性,易受环境因素和表面状态影响。
两者在科研、工业质检中常需同时测试,以全面评估材料的电学性能(如高压绝缘材料需高体积电阻率 高表面电阻,而防静电材料需中等体积电阻率 低表面电阻)。
业务咨询:932174181 媒体合作:2279387437 24小时服务热线:15136468001 盘古机械网 - 全面、科学的机械行业免费发布信息网站 Copyright 2017 PGJXO.COM 豫ICP备12019803号