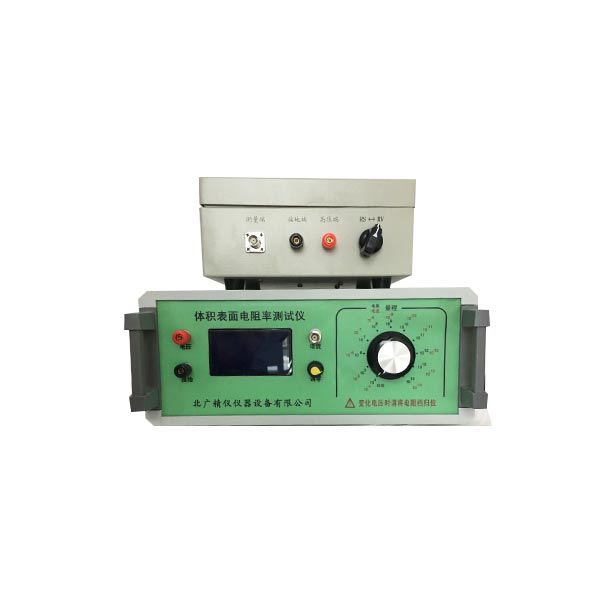
高绝缘电阻测量仪-表面电阻率测试仪 高绝缘电阻测量仪用于测量绝缘材料、电工产品、各种元器件的绝缘电阻;与恒温水浴配套后,还能测量不同温度下的塑料电线电缆(无屏蔽层)的绝缘电阻,该仪器具有测量精度高、性能稳定、操作简单、输入端高压短路等优点,仪器的高量程1018Ω电阻值(测试电压为1000V)
高绝缘电阻测量仪-表面电阻率测试仪 技术指标
1. 电阻测量范围:1?104Ω~1?1018Ω,分为十个量程。
2. 电流测量范围为2?10-4A~1?10-16A
3. 全数字液晶屏显示。
4. 准确度:准确度优于下表
量程有效显示范围20~30℃ RH<80%
104 0.01~19.99 5%
105 0.01~19.99 5%
106 0.01~19.99 5%
107 0.01~19.99 5%
108 0.01~19.99 5%
109 0.01~19.99 5%
1010 0.01~19.99 5% 2字
1011 0.01~19.99 5% 2字
1012 0.01~19.99 5% 5字
1013 0.01~19.99 10% 5字
1014 0.01~19.99 10% 5字
1014以上0.01~19.99 10-15% 5字
超出有效显示范围时误差有可能增加,测试电流准确度与电阻相同,测试电压准确度为10%
5.使用环境:温度-10℃~50℃相对湿度<90%。
6.测试电压: DC10V、50V、100V、250V、500V、1000V。?10%
7.供电形式: AC 220V,50HZ,功耗约10W。
8.仪器尺寸: 300mm? 280mm? 150 mm。
9.质量:约3.0KG。
说明
1.电阻率ρ不仅和导体的材料有关,还和导体的温度有关。在温度变化不大的范围内:几乎所有金属的电阻率随温度作线性变化,即ρ=ρo(1 at)。式中t是摄氏温度,ρo是O℃时的电阻率,a是电阻率温度系数。
2.由于电阻率随温度改变而改变,所以对于某些电器的电阻,必须说明它们所处的物理状态。如一个220 V -100 W电灯灯丝的电阻,通电时是484欧姆,未通电时只有40欧姆左右。
3.电阻率和电阻是两个不同的概念。电阻率是反映物质对电流阻碍作用的属性,电阻是反映物体对电流阻碍作用的能力大小。
4.超导体的直流电阻率在一定的低温下突然消失,被称作零电阻效应。导体没有了电阻。
电阻的作用:
电阻在电路中的作用:利用著名的欧姆定律可以利用电阻控制电路中的电压、电流。
电阻的主要物理特征就是可以变电能为热能,因此热水器中的发热元件、电灯泡、电烫斗就是利用了电阻的作用制成的。另外电阻有怕热的特性,当导体材料温度升高时材料的电阻率会增大(有些材料则表现为减小),因此利用电阻的这种特性可以制作温度测量计(不知道你看见过没,插一根“铁丝”就能测量温度的方法就是利用了这种电阻材料作用的)。
另外一些材料的电阻还会受到光线照射的印象,而利用这样的材料可以制成光敏电阻,利用这点作用可以方便的设计光控电路以及光的测量和光电转换等领域。
报告
报告应至少包括下述情况:
a)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)关于材料的说明和标志(名称、等级、颜色、制造商等);
b)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)试样的形状和尺寸;
c)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)电极和保护装置的形式、材料和尺寸;
d)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)试样的处理(清洁、预干燥、处理时间、湿度和温度)等;
e)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)试验条件(试样温度、相对由度);
f)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)测量方法;
g)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)施加电压;
h)电阻率测试仪(电阻率测定仪)体和、电阻率(需要时);
注1:当规定了一个固定的电化时间时,注明此时间,给出个别值,并报告中值作为体积电阻率。
注2: 当在不同的电化时间后测试时,应按如下要求报告:
当在相同的电化时间里试样达到一个稳定状态肘,给出个别值,并报告中值作为体积电阻率。在这个电化时间里有某些试样不能达到稳定状态,则报告不能达到稳定状态的试样数,并分别地给出它们的结果。当测试结果取决于电化时间时,则报告它们之间的关系,例如.以图的形式或给出在电化Imin、10min和100min后的体积电阻率的中值。
i)表面电阻率(需要时):
给出电化时间为1 min的个别值,并报告其中值作为表面电阻率。
方法
测量高电阻常用的方法是直接法或比较法。
直接法是测量加在试样上的直流电压和流过它的电流(伏安法)而求得未知电阻。
比较法是确定电桥线路中试样未知电阻与电阻器已知电阻之间的比值,或是在固定电压下比较通过这两种电阻的电流。
附录A给出了描述这些原理的例子。
伏安法需要一适当精度的伏特表,但该方法的灵敏度和度主要取决于电流测量装置的性能,该装置可以是一个检流计或电子放大器或静电计。
电桥法只需要一灵敏的电流检测器作为零点指示器,测量度主要取决于已知的桥臂电阻器,这些桥臂电阻应在宽的电阻值范围内具有高的精密度和稳定性。
电流比较法的度取决于已知电阻器的度和电流测量装置,包括与它相连的测量电阻器的稳定度和线性度。只要电压是恒定的,电流的确切数值并不重要。
对于不大于1011Ω的电阻,可以按照11.1用检流计采用伏特计一安培计法来测定其体积电阻率。 对于较高的电阻,则推荐使用直流放大器或静电计。
在电桥法中,不可能直接测量短路试样中的电流(见11.1)。
利用电流测量装置的方法可以自动记录电流,以简化稳态测试过程(见11.1)。
现己有测量高电阻的一些专门的线路和仪器。只要它们有足够的度和稳定度,且在需要时能使试样短路并在电化前测量电流者,均可使用。
典型应用
1测量防静电鞋、导电鞋的电阻值
按照国家标准GB4386-84《防静电胶底鞋(靴)、导电胶底鞋(靴)电阻值测量方法》防静电鞋的电阻值必须为0.5.?105Ω1.0?108Ω范围内,导电鞋的电阻值必须不大于1.5X105欧姆.不仅制造厂在出厂时必须按这一标准检验,合格后才能出厂,在工厂使用过程中也必须按这一标准进行定期检验,合格后才能穿用。
制造厂测量新鞋的电阻值时,应将硫化后有新鞋放置24小时以上,然后在测量所要求的温度、湿度环境中放置2小时以后才能进行测量。使用单位在定期检测时应将鞋洗干净,其温湿度的要求及放置时间同上。测量环境要求为:温度:10℃~40℃相对湿度为40%~70%。 由于HEST121型数字表面、体积电阻率测定仪是内部同时测量电压和电流,且直接显示出电阻值,所以不必另外使用电压表和电流表以及计算电阻值。
通常测试防静电鞋只用106、107、108Ω档,测试完毕将开关拨回104档。
根据上述测试的结果,根据标准来确定被测鞋是否合格或能否穿用。
2.测量防静电材料的电阻及电阻率
一般防静电材料的电阻值在105 Ω~1010 Ω左右的范围内,其测量电极可采用三电极或二电极,其具体测量方法可参照有关的标准或有关资料。
3.测量计算机房用活动地板的系统电阻值
按照国家标准GB6650-86《计算机房用活动地板技术条件》。采用该标准的电极(也可用三电极中的主电极)测量。
4.测量绝缘材料电阻(率)
绝缘材料如塑料(聚乙稀,聚氯乙稀,尼龙等)橡胶等的电阻率很高,测量时应采取屏蔽措施,以免读数不稳甚至无法测量。测量时可采用三电极。具体方法可参照国家标准GB1410。
5.测量电流及1014Ω以上超高电阻的测量
当测量超过1014Ω以上的超高电阻时,可以通过测量电流的方法,然后用欧姆
定律求出超高电阻值。测量电流与测量电阻的方法基本相同,
例如:电流表头显示读数为1.234,量程位置处在10-8,则电流为I=1.234?10-8 A
利用欧姆定律
V
R= ---
I
可以计算出电阻值。利用测量电流的方法可测量超过1014Ω以上的超高电阻1015~1018Ω。
describe
The resistivity ρ is not only related to the material of the conductor, but also to the temperature of the conductor. In the range where temperature changes little: the resistivity of almost all metals varies linearly with temperature, that is, ρ=ρ o (1 at). In the formula, t is the temperature in Celsius, ρ o is the resistivity at O ℃, and a is the temperature coefficient of resistivity.
2. As the resistivity changes with temperature, it is necessary to explain the physical state of the resistance of certain electrical appliances. The resistance of a 220 V -100 W electric lamp filament is 484 ohms when powered and only about 40 ohms when not powered.
3. Electrical resistivity and resistance are two different concepts. Electrical resistivity is a property that reflects the obstruction of current by a substance, and resistance is the ability of an object to obstruct current.
The sudden disappearance of the DC resistivity of superconductors at a certain low temperature is called the zero resistance effect. The conductor has lost its resistance.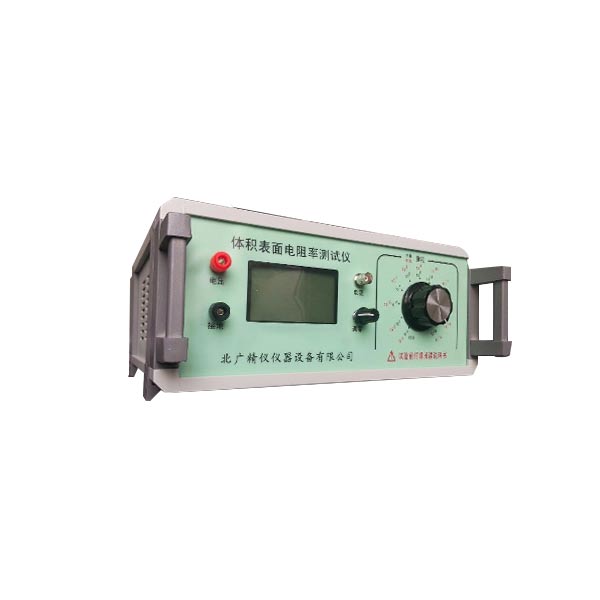


The function of resistance:
The role of resistance in circuits: Using the famous Ohm's law, resistance can be used to control the voltage and current in a circuit.
The main physical characteristic of resistance is that it can convert electrical energy into thermal energy, so the heating elements, light bulbs, and electric irons in water heaters are made using the effect of resistance. In addition, resistors have the characteristic of being sensitive to heat. When the temperature of the conductor material increases, the resistivity of the material will increase (some materials show a decrease). Therefore, using this characteristic of resistors can be used to make temperature measuring instruments (I don't know if you have seen it, the method of measuring temperature by inserting a "wire" is based on the effect of this resistor material).
In addition, the resistance of some materials can also be affected by light exposure, and using such materials can make photoresistors. This can facilitate the design of light control circuits, as well as the measurement and photoelectric conversion of light.
report
The report should include at least the following information:
a) Description and marking of materials (name, grade, color, manufacturer, etc.) for resistivity tester (resistivity tester);
b) The shape and size of the sample of the resistivity tester (resistivity tester);
c) The form, material, and size of electrodes and protective devices for resistivity testers (resistivity meters);
d) Processing of resistivity tester (resistivity tester) samples (cleaning, pre drying, processing time, humidity, and temperature), etc;
e) Test conditions for resistivity tester (resistivity tester) (sample temperature, relative humidity);
f) Measurement method of resistivity tester (resistivity measuring instrument);
g) Apply voltage to the resistivity tester;
h) Electrical resistivity tester (resistivity tester) body and resistivity (when needed);
Note 1: When a fixed electrification time is specified, indicate this time, provide individual values, and report the median as the volume resistivity.

Note 2: When testing after different electrification times, the following requirements should be reported:
When the sample reaches a stable state elbow within the same electrochemical time, provide individual values and report the median as the volume resistivity. If some samples cannot reach a stable state during this electrification time, report the number of samples that cannot reach a stable state and provide their results separately. When the test results depend on the electrification time, report the relationship between them, for example, in the form of a graph or provide the median volume resistivity after electrification for Imin, 10min, and 100min.
i) Surface resistivity (when needed):
Provide individual values with an electrochemical time of 1 minute and report the value as the surface resistivity.
method
The commonly used methods for measuring high resistance are direct method or comparative method.
The direct method is to measure the DC voltage applied to the sample and the current flowing through it (volt ampere method) to obtain the unknown resistance.
The comparative method is to determine the ratio between the unknown resistance of the sample in the bridge circuit and the known resistance of the resistor, or to compare the current passing through these two resistors at a fixed voltage.
Appendix A provides examples to describe these principles.
The volt ampere method requires a voltmeter of appropriate accuracy, but the sensitivity and accuracy of this method mainly depend on the performance of the current measuring device, which can be a galvanometer, electronic amplifier, or electrostatic meter.
The bridge method only requires a sensitive current detector as a zero point indicator, and the measurement accuracy mainly depends on the known bridge arm resistors, which should have high precision and stability over a wide range of resistance values.
The degree of current comparison method depends on the known degree of the resistor and the current measuring device, including the stability and linearity of the measuring resistor connected to it. As long as the voltage is constant, the exact value of the current is not important.
For resistors not exceeding 1011 Ω, the volume resistivity can be measured using a voltmeter ammeter method according to 11.1. For higher resistance, it is recommended to use a DC amplifier or an electrostatic meter.
In the bridge method, it is not possible to directly measure the current in the short-circuit specimen (see 11.1).
The method of using a current measuring device can automatically record the current to simplify the steady-state testing process (see 11.1).
There are now some specialized circuits and instruments for measuring high resistance. As long as they have sufficient degree and stability, and can short-circuit the sample and measure the current before electrification when needed, they can be used.
体积电阻率与表面电阻的区别
体积电阻率和表面电阻是材料电学性能的两个重要参数,但两者针对的测试对象和应用场景不同。以下是两者的主要区别:
1. 定义与物理意义
体积电阻率(Volume Resistivity)
体积电阻率是衡量材料内部导电性能的参数,表示单位体积材料对电流的阻碍能力。
体积电阻率反映材料本身的绝缘或导电特性,与材料的成分、结构及温度密切相关。例如,绝缘塑料的 可达12次方-16次方,而金属的 仅为 10的-6}- 10^-4次方 。
表面电阻(Surface Resistance)
表面电阻是衡量材料表面导电性能的参数,表示电流沿材料表面流动时的阻碍能力。
表面电阻受材料表面状态(如污染、湿度、氧化层)影响显著,常用于评估材料的防静电性能或漏电风险。
2. 测量方法与电极配置
-体积电阻率测量
- 电极设计:使用三电极系统(如保护环电极),确保电流仅通过材料内部,避免表面电流干扰。
- 测试标准:如 ASTM D257、IEC 60093。
- 适用场景:块状固体材料(如塑料、陶瓷、橡胶)的绝缘性能评估。
- 表面电阻测量
-电极设计:采用平行电极或同心环电极,使电流沿材料表面流动。
-测试标准:如 ASTM D4496、IEC 61340。
-适用场景:薄膜、涂层、纺织品等表面导电性能测试,或防静电材料的筛选。
3. 应用领域差异
参数
体积电阻率:
核心用途评估材料内部绝缘
典型应用电线绝缘层、电子封装材料、高压设备
关键影响因素材料成分、温度、杂质浓度
表面电阻:评估材料表面导电/防静电性能 导电性
影响因素表面清洁度、湿度、污染、氧化层
4. 实例对比
绝缘塑料板:
体积电阻率高于15次方,说明内部绝缘性能优异;
- 表面电阻可能因吸附水分而降低于12次方,表明表面存在微弱导电性。
5. 总结
体积电阻率:表征材料整体的绝缘或导电能力,是材料本征属性的体现。
表面电阻:反映材料表面的导电特性,易受环境因素和表面状态影响。
两者在科研、工业质检中常需同时测试,以全面评估材料的电学性能(如高压绝缘材料需高体积电阻率 高表面电阻,而防静电材料需中等体积电阻率 低表面电阻)。
业务咨询:932174181 媒体合作:2279387437 24小时服务热线:15136468001 盘古机械网 - 全面、科学的机械行业免费发布信息网站 Copyright 2017 PGJXO.COM 豫ICP备12019803号