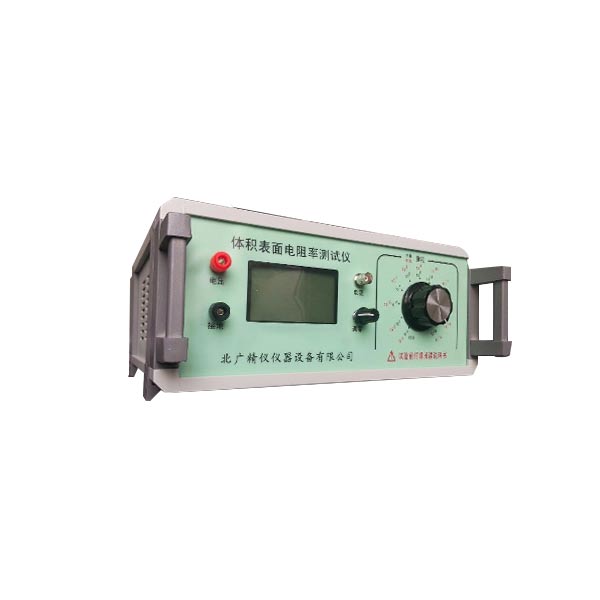
塑料表面体积电阻率测定仪厂家 技术参数:
1、电阻测量范围1?104Ω~1?1018Ω
2、电流测量范围2?10-4A~1?10-16A
3、显 示 方 式 数字液晶显示
4、内置测试电压10V、50V、100V、250V、500V、1000V
5、基本准确度1%
6、使用环境 温度:0℃~40℃,相对湿度<80%
7、供电形式AC 220V,50HZ,功耗约5W
8、仪器尺寸285mm? 245mm? 120 mm
9、质量约5KG
10、体积小、重量轻、准确度高电阻、电流双显示,性能好稳定、读数方便
11、使测量超高电阻就如用万用表测量普通电阻样简便免去老式高阻计在不同测试电压下或不同量程时要乘以系数等使用不便的麻烦
塑料薄膜电阻率测定仪既可测量高电阻,又可测微电流。采用了美国Intel公司的大规模集成电路,使仪器体积小、重量轻、准确度高。以双3.1/2位数字直接显示电阻的高阻计和电流。量限从1?104Ω~1?1018 Ω,是目前国内测量范围 宽,准确度 高的数字超高阻测量仪。
塑料表面体积电阻率测定仪厂家 材料说明
A、通常,绝缘材料用于电气系统的各部件相互绝缘和对地绝缘,固体绝缘材料还起机械支撑作用.一般希望材料有尽可能高的绝缘电阻,并具有合适的机械、化学和耐热性能.
B、体积电阻班组可作为选择绝缘材料的一个参数,电阻率随温度和湿度的京戏化而显著变化.体积电阻率的测量常常用来检查绝缘材料是否均匀,或都用来检测那些能影响材料质量而又不能作其他方法检测到的导电杂质.
C、当直流电压加到与试样接触的两电极间时,通过试样的电流会指数式地衰减到一个稳定值.电流随时间的减小可能是由于电介质极化和可动离子位移到电极所致.对于体积电阻小于10的10Ω.m
的材料,其稳定状态通常在1min内达到.因此,要经过这个电化时间后测定电阻.对于电阻率较高的材料,电流减小的过程可能会持续几分钟、几小时、几天,因此需要用较长的电化时间.如果需要的话,可用体积电阻率与关系来描述材料的特性.

D、由于体积电阻总是要被或多或少地包括到表面电阻的测试中去,因些近似地测量表面电阻,测得的表面电阻值主要反映被测试样表面污染的程度.所以,表面电阻率不是表面材料本身特性的参数,而是一个有关材料表面污染特性的参数.
当表面电阻较高时,它常随时间以不规则的方式变化.测量表面电阻通常都规定11min的电化时间.
试样处置
电极之间或测量电极与大地之间的杂散电流对于测试仪器的读数没有明显的影响这一点很重要。测试时加电极到试样上和安放试样时均要极为小心,以免可能产生对测试结果有不良影响的杂散电流通道。
测量表面电阻时,不要清洗表面,除非另有协议或规定。除了同二材料的另一个试样的未被触模过的表面可触及被测试样外,表面被测部分不应被任何东西触及。
什么是电阻率?
电阻跟导体的材料、横截面积、长度有关。
导体的电阻与两端的电压以及通过导体的电流无关。
导体电阻跟它长度成正比,跟它的横截面积成反比.
(1)定义或解释
电阻率是用来表示各种物质电阻特性的物理量。用某种材料制成的长为1米、横截面积为1mm2米。的导体的电阻,在数值上等于这种材料的、电阻率。
(2)单位
在国际单位制中,电阻率的单位是欧姆?米。一般常用的单位是欧姆?毫米2/米。

(3)说明
①电阻率ρ不仅和导体的材料有关,还和导体的温度有关。在温度变化不大的范围内,几乎所有金属的电阻率随温度作线性变化,即ρ=ρo(1 at)。式中t是摄氏温度,ρo是O℃时的电阻率,a是电阻率温度系数。
②由于电阻率随温度改变而改变,所以对于某些电器的电阻,必须说明它们所处的物理状态。如一个220V
100W电灯灯丝的电阻,通电时是484欧姆,未通电时只有40欧姆左右。
③电阻率和电阻是两个不同的概念。电阻率是反映物质对电流阻碍作用的属性,电阻是反映物体对电流阻碍作用的属性。
What is electrical resistivity?
Resistance is related to the material, cross-sectional area, and length of the conductor.
The resistance of a conductor is independent of the voltage at both ends and the current passing through the conductor.
The resistance of a conductor is directly proportional to its length and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area
(1) Definition or Explanation
Electrical resistivity is a physical quantity used to represent the resistance characteristics of various substances. Made of a certain material with a length of 1 meter and a cross-sectional area of 1mm2. The resistance of a conductor is numerically equal to the resistivity of this material.
(2) Unit
In the International System of Units, the unit of electrical resistivity is ohms per meter. The commonly used unit is ohm ? mm2/meter.

(3) Explanation
① The resistivity ρ is not only related to the material of the conductor, but also to the temperature of the conductor. Within a range where temperature does not change significantly, the resistivity of almost all metals varies linearly with temperature, i.e., ρ=ρ o (1 at). In the formula, t is the temperature in Celsius, ρ o is the resistivity at O ℃, and a is the temperature coefficient of resistivity.
② Due to the change in resistivity with temperature, it is necessary to explain the physical state of the resistance of certain electrical appliances. Like a 220V
The resistance of a 100W electric lamp filament is 484 ohms when powered on and only about 40 ohms when not powered on.
③ Electrical resistivity and resistance are two different concepts. Electrical resistivity is a property that reflects the obstruction of current by a substance, while resistance is a property that reflects the obstruction of current by an object.
电极材料
8.1概述
绝缘材料用的电极材料应是一类容易加到试样上、能与试样表面紧密接触、且不致于因电极电阻或对试样的污染而引入很大误差的导电材料。在试验条件下,电极材料应能耐腐蚀。下面是可使用的一些典型的电极材料。电极应与给定形状和尺寸的合适的背衬电极一同使用。
简便的做法是用两种不同的电极材料或两种不同的使用方法来了解电极材料是否会引人很大误差。
8.2导电银漆
某些高导电率的商品银漆,无论是气干的或低温烘干的,是足够疏松的、能透过温气,因此可在加上电极后对试样进行条件处理。这种特点特别适合研究电阻湿气效应以及电阻随温度的变化。然而,在导电漆被用作一种电极材料以前,应证实漆中的潜剂不影响试样的电性能。用精巧的毛刷可做到使保护电极的边缘相当光滑。但对于圆电极,可先用圆规画出电极的轮廊,然后用刷子来涂满内部的方法来获得精细的边缘。如电极漆是用喷枪喷上去的,则可采用固定模框。
8.3喷镀金属
可使用能满意地粘合在试样上的喷镀金属。薄的喷镀电极的优点是一旦喷在试样上便可立即使用。这种电极或许是足够疏松的,可允许对试样进行条件处理,但这→特点应被证实。固定的模框可用 来制取被保护电极与保护电极之间的间隙。
8.4蒸发或阴极真空喷镀金属
当能证明材料不受离子轰击或真空处理的影响时,蒸发或阴极真空喷镀金属能在与8. 3给出的相同条件下使用。
8.5液体电极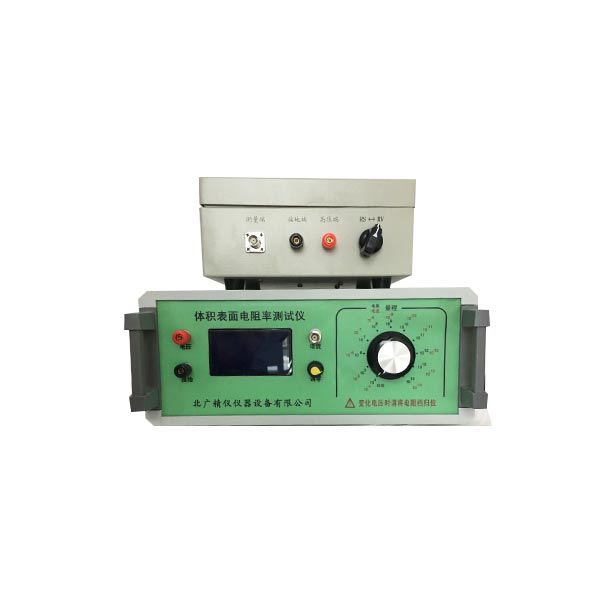
使用液体电极往往能得到满意的结果。构成上电极的液体应被框住,例如用不锈钢环来框住,每个环的下边缘在不接触液体的一面被斜削成锐边。图4给出了使用液体电极的装置。 不推荐长期使用或 在高温下使用水银,因为它有毒。
8.6胶体石墨
分散在水中或其他合适媒质中的肢体石墨可在与8. 2给出的相同条件下使用。
8. 7导电橡皮
导电橡皮可用作电极材料。它的优点是能方便快捷地放上和移开。由于只是在测定时才将电极放到试祥上,因此它不妨碍试样的条件处理。导电橡皮应足够柔软,以确保其在加上适当的压力例如2 kPa(O. 2 N/cm2)时能与试样紧密接触。
8.8金属锚
金属锚可粘贴在试样表面作为测量体积电阻用的电极,但它不适用于测量表面电阻。铅、锦铅合金、铝和锡锚都是被普遍使用的。通常用少量的凡士林、硅脂、硅油或其他合适的材料作为粘贴剂将它们粘贴到试样上去。含有下列组分的一种药用胶适合用作导电粘贴剂:
分子量为600的无水聚乙二醇800份(质量)
水200份(质量)
软肥皂(药用级)1份(质量)
氧化钾
要在一个平稳的压力下粘贴电极,使之足以消除一切皱折和将多余的粘合剂赶到筒的边缘,再用一块干净的薄纸擦去。用软物如手指按压能很好地做到这点。这个技巧仅适用于表面非常平滑的试样。通过精心操作,粘合剂薄层可减小到0. 002 5 mm或更薄。
Electrode material
8.1 Overview
The electrode material used for insulation materials should be a conductive material that is easy to apply to the sample, can be in close contact with the sample surface, and does not introduce significant errors due to electrode resistance or contamination of the sample. Under experimental conditions, the electrode material should be corrosion-resistant. Here are some typical electrode materials that can be used. The electrode should be used with a suitable backing electrode of the given shape and size.
A simple approach is to use two different electrode materials or two different usage methods to determine whether the electrode material will introduce significant errors.
8.2 Conductive Silver Paint
Some high conductivity silver paints, whether air dried or low-temperature dried, are sufficiently loose and can pass through warm air, so they can be conditioned on the sample after adding electrodes. This characteristic is particularly suitable for studying the moisture effect of resistance and the variation of resistance with temperature. However, before using conductive paint as an electrode material, it should be confirmed that the latent agent in the paint does not affect the electrical properties of the sample. Using a delicate brush can make the edges of the protective electrode quite smooth. But for circular electrodes, you can first draw the contour of the electrode with a compass, and then use a brush to coat the inside to obtain fine edges. If the electrode paint is sprayed with a spray gun, a fixed mold frame can be used.
8.3 Metal spraying
Spray metal that can be satisfactorily adhered to the sample can be used. The advantage of thin spray coated electrodes is that they can be used immediately once sprayed onto the sample. This type of electrode may be loose enough to allow for conditioning of the sample, but this characteristic should be confirmed. A fixed mold frame can be used to create a gap between the protected electrode and the protective electrode.
8.4 Evaporation or cathodic vacuum deposition of metals
When it can be proven that the material is not affected by ion bombardment or vacuum treatment, evaporation or cathodic vacuum deposition of metals can be compared to 8 Use under the same conditions as given in 3.
8.5 Liquid electrode
The use of liquid electrodes often yields satisfactory results. The liquid that constitutes the upper electrode should be framed, for example, with stainless steel rings, and the lower edge of each ring should be chamfered to a sharp edge on the side that does not come into contact with the liquid. Figure 4 shows the device using liquid electrodes. It is not recommended to use mercury for a long time or at high temperatures because it is toxic.
8.6 Colloidal graphite
Limb graphite dispersed in water or other suitable media can be used in conjunction with 8 Use under the same conditions as given in 2.
8.7 Conductive rubber
Conductive rubber can be used as electrode material. Its advantage is that it can be easily and quickly placed on and removed. Since the electrode is only placed on the test sample during the measurement, it does not hinder the conditioning of the sample. The conductive rubber should be soft enough to ensure close contact with the sample when subjected to appropriate pressure, such as 2 kPa (0.2 N/cm2).
8.8 Metal Anchor
Metal anchors can be attached to the surface of the specimen as electrodes for measuring volume resistance, but they are not suitable for measuring surface resistance. Lead, lead alloy, aluminum, and tin anchors are commonly used. Usually, a small amount of Vaseline, silicone grease, silicone oil, or other suitable materials are used as adhesives to stick them to the sample. A medicinal adhesive containing the following components is suitable for use as a conductive adhesive:
800 parts (mass) of anhydrous polyethylene glycol with a molecular weight of 600
200 parts of water (by quality)
1 serving of soft soap (medicinal grade) (quality)
Potassium oxide
To paste the electrode under a steady pressure, it is necessary to eliminate all wrinkles and push excess adhesive to the edge of the cylinder, and then wipe it off with a clean thin paper. Pressing with soft objects such as fingers can achieve this very well. This technique is only applicable to samples with very smooth surfaces. Through careful operation, the thin layer of adhesive can be reduced to 0 002 5mm or thinner.
符合标准
GB/T 1410-2006、GB 12014、GB/T 20991-2007、GB 4385-1995、GB 12158-2006、GB 4655-2003、GB/T 12703.4-2010、GB/T 12703.6-2010、GB 13348-2009、GB/T 15738-2008、GB/T 18044-2008、GB/T 18864-2002、GB/T 22042-2008、GB/T 22043-2008、GB/T 24249-2009、GB 26539-2011、GB/T 26825-2011、GB 50515-2010、GB 50611-2010、GJB 105-1998-Z、GJB 3007A-2009、GJB 5104-2004
标准配置:
1、仪器主机 一台
2、屏蔽箱一个
3、试验电极三个
4、说明书一本
5、电源线一条
6、数据线三条
7、合格证一份
8、保修卡一份
体积电阻率与表面电阻的区别
体积电阻率和表面电阻是材料电学性能的两个重要参数,但两者针对的测试对象和应用场景不同。以下是两者的主要区别:
1. 定义与物理意义
体积电阻率(Volume Resistivity)
体积电阻率是衡量材料内部导电性能的参数,表示单位体积材料对电流的阻碍能力。
体积电阻率反映材料本身的绝缘或导电特性,与材料的成分、结构及温度密切相关。例如,绝缘塑料的 可达12次方-16次方,而金属的 仅为 10的-6}- 10^-4次方 。
表面电阻(Surface Resistance)
表面电阻是衡量材料表面导电性能的参数,表示电流沿材料表面流动时的阻碍能力。
表面电阻受材料表面状态(如污染、湿度、氧化层)影响显著,常用于评估材料的防静电性能或漏电风险。
2. 测量方法与电极配置
-体积电阻率测量
- 电极设计:使用三电极系统(如保护环电极),确保电流仅通过材料内部,避免表面电流干扰。
- 测试标准:如 ASTM D257、IEC 60093。
- 适用场景:块状固体材料(如塑料、陶瓷、橡胶)的绝缘性能评估。
- 表面电阻测量
-电极设计:采用平行电极或同心环电极,使电流沿材料表面流动。
-测试标准:如 ASTM D4496、IEC 61340。
-适用场景:薄膜、涂层、纺织品等表面导电性能测试,或防静电材料的筛选。
3. 应用领域差异
参数
体积电阻率:
核心用途评估材料内部绝缘
典型应用电线绝缘层、电子封装材料、高压设备
关键影响因素材料成分、温度、杂质浓度
表面电阻:评估材料表面导电/防静电性能 导电性
影响因素表面清洁度、湿度、污染、氧化层
4. 实例对比
绝缘塑料板:
体积电阻率高于15次方,说明内部绝缘性能优异;
- 表面电阻可能因吸附水分而降低于12次方,表明表面存在微弱导电性。
5. 总结
体积电阻率:表征材料整体的绝缘或导电能力,是材料本征属性的体现。
表面电阻:反映材料表面的导电特性,易受环境因素和表面状态影响。
两者在科研、工业质检中常需同时测试,以全面评估材料的电学性能(如高压绝缘材料需高体积电阻率 高表面电阻,而防静电材料需中等体积电阻率 低表面电阻)。
业务咨询:932174181 媒体合作:2279387437 24小时服务热线:15136468001 盘古机械网 - 全面、科学的机械行业免费发布信息网站 Copyright 2017 PGJXO.COM 豫ICP备12019803号